Using data science and advanced DNA, RNA & trait technologies to better understand genetic and phenotypic variation as the basic source for crop improvement
Genetic variation is the fundamental source for crop improvement. So, it is essential to understand the genetic diversity and to develop crop varieties that meet the current needs of growers, consumers and our other partners in the agricultural food business.
KeyGene deploys proprietary data science and DNA & RNA technologies to generate genomic insights that can benefit breeders and scientists alike.
Our specialists in metabolomics and proteomics identify the optimal starting points and research approaches to help our partners best understand the “omics” variation available to them and most likely to meet their needs. By linking this variation to plant traits, we support our partners to increase the speed and effectiveness of crop improvement programs and boost breeding efficiency.
Ours is a dual approach of providing better insights into the link between DNA & RNA, protein, and metabolites on the one hand – and a crop’s traits on the other – to help our partners advance their crop improvement efforts.
Technological innovation
To that end, KeyGene continuously develops proprietary know-how in the fields of DNA & RNA technology, metabolomics & proteomics, trait research and data science to address our partners’ toughest R&D and breeding challenges.
Technological innovations like KeyGene’s data integration and visualization package – CropPedia – are transferred to our partners for in-house use when it is beneficial.
Examples of KeyGene's contribution to revealing and understanding variation
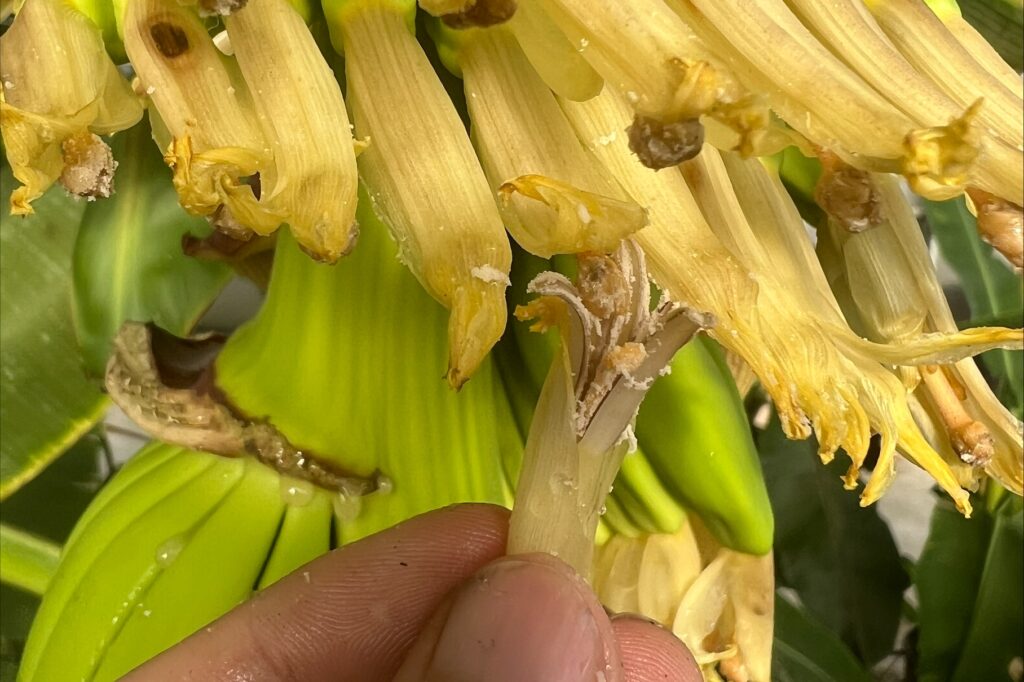

Banana research & breeding at KeyGene
In 2017 we decided to invest in banana breeding and research, because we trusted we could have a substantial positive impact on the disease problems in banana. Since then, partners…